Continuation
In computer science and programming, a continuation is an abstract representation of the control state of a computer program. A continuation reifies the program control state, i.e. the continuation is a data structure that represents the computational process at a given point in the process' execution; the created data structure can be accessed by the programming language, instead of being hidden in the runtime environment. It contains information such as the process' current stack (including all data whose lifetime is within the process e.g. "local variables"), as well as the process' point in the computation. An instance of continuation can be later used as a control structure; upon invocation, it will resume execution from the control point that it represents. The "current continuation" or "continuation of the computation step" is the continuation that, from the perspective of running code, would be derived from the current point in a program's execution.
The term continuations can also be used to refer to first-class continuations, which are constructs that give a programming language the ability to save the execution state at any point and return to that point at a later point in the program.
Programs must allocate space in memory for the variables its functions use. Most programming languages use a call stack for storing the variables needed because it allows for fast and simple allocating and automatic deallocation of memory. There are also programming languages that use a heap for this, which allows for flexibility but with a higher cost for allocating and deallocating memory. These two different implementations both have benefits and drawbacks in the context of continuations.[1]
Almost all languages have a means for manipulating the order of execution steps (i.e. manipulating the continuation of a computation step). The goto is the most basic form of this. Control structures such as if statements, loops, return statements, break statements, and exit are more structured (and limited) ways to manipulate the order of executing instructions and are essentially limited goto statements.
More complex constructs exist as well, for which "continuations provide an elegant description".[2] For example in C, setjmp can be used to jump from the middle of one function to another function, provided the second function lies deeper in the stack (if it is waiting for the first function to return, possibly among others). Other more complex examples include coroutines in Simula 67, Lua, and Perl; tasklets in Stackless Python; generators in Icon and Python; continuations in Scala (starting in 2.8); fibers in Ruby (starting in 1.9.1); the backtracking mechanism in Prolog; monads in functional programming; and threads.
Contents |
History
The earliest description of continuations was made by Adriaan van Wijngaarden in September 1964. Wijngaarden spoke at the IFIP Working Conference on Formal Language Description Languages held in Baden bei Wien, Austria. As part of a formulation for an Algol 60 preprocessor, he called for a transformation of proper procedures into continuation-passing style.[2]
Christopher Strachey, Christopher P. Wadsworth and John C. Reynolds brought the term continuation into prominence in their work in the field of denotational semantics that makes extensive use of continuations to allow sequential programs to be analysed in terms of functional programming semantics.[2]
Steve Russell invented the continuation in his second Lisp implementation for the IBM 704, though he did not name it.[3]
A complete history of the discovery of continuations is given by (Reynolds 1993).
First-class continuations
First-class continuations are a language's ability to completely control the execution order of instructions. They can be used to jump to a function that produced the call to the current function, or to a function that has previously exited. One can think of a first-class continuation as saving the state of the program. However, it is important to note that true first-class continuations do not save program data, only the execution context. This is illustrated by the "continuation sandwich" description:
Say you're in the kitchen in front of the refrigerator, thinking about a sandwich. You take a continuation right there and stick it in your pocket. Then you get some turkey and bread out of the refrigerator and make yourself a sandwich, which is now sitting on the counter. You invoke the continuation in your pocket, and you find yourself standing in front of the refrigerator again, thinking about a sandwich. But fortunately, there's a sandwich on the counter, and all the materials used to make it are gone. So you eat it. :-)[4]
Scheme was the first full production system, providing first "catch"[2] and then call/cc. Bruce Duba introduced call/cc into SML.
Continuations are also used in models of computation including denotational semantics, the Actor model, process calculi, and lambda calculus. These models rely on programmers or semantics engineers to write mathematical functions in the so-called continuation-passing style. This means that each function consumes a function that represents the rest of the computation relative to this function call. To return a value, the function calls this "continuation function" with a return value; to abort the computation it returns a value.
Functional programmers who write their programs in continuation-passing style gain the expressive power to manipulate the flow of control in arbitrary ways. The cost is that they must maintain the invariants of control and continuations by hand, which is a highly complex undertaking.
Uses
Continuations are useful because they simplify and clarify the implementation of several other common programming design patterns, including coroutines (aka green threads), and exception handling. Continuations provide the basic, low-level primitive unifying these otherwise seemingly unconnected patterns. Continuations can provide elegant solutions to some difficult high-level problems, in particular the problem of programming a web server that supports multiple pages, accessed by the user's use of the forward and back buttons and by following links. The Seaside web framework in Smalltalk uses continuations to great effect, allowing one to program the web server in procedural style, by switching continuations when switching pages.
Examples
The Scheme programming language includes the control operator call-with-current-continuation (abbreviated as: call/cc) with which a Scheme program can manipulate the flow of control:
; call/cc calls its first function argument, passing ; a continuation variable representing this point in ; the program as the argument to that function. ; ; In this case, the function argument assigns that ; continuation to the variable the-continuation. ; ; ; The next time the-continuation is called, we start here.
Defines a function test that sets the-continuation to the future execution state of itself:
> (test)
1
> (the-continuation)
2
> (the-continuation)
3
> ; stores the current continuation (which will print 4 next) away
> (define another-continuation the-continuation)
> (test) ; resets the-continuation
1
> (the-continuation)
2
> (another-continuation) ; uses the previously stored continuation
4
For a gentler introduction to this mechanism, see call-with-current-continuation.
Coroutines
This example shows a possible usage of continuations to implement coroutines as separate threads.[5]
;;; A naive queue for thread scheduling. ;;; It holds a list of continuations "waiting to run". ;;; This starts a new thread running (proc). ;;; This yields the processor to another thread, if there is one. ;;; This terminates the current thread, or the entire program ;;; if there are no other threads left.
The functions defined above allow for defining and executing threads through cooperative multitasking, i.e. threads that yield control to the next one in a queue:
;;; The body of some typical Scheme thread that does stuff: "~A ~A\n";;; Create two threads, and start them running. "This is AAA""Hello from BBB"
The previous code will produce this exit:
This is AAA 0 Hello from BBB 0 This is AAA 1 Hello from BBB 1 This is AAA 2 Hello from BBB 2 ...
Programming language support
Many programming languages exhibit first-class continuations under various names; specifically:
- C:
setcontextet al. (POSIX) - Java: Lightwolf
- Factor:
callcc0andcallcc1 - Haskell: The Continuation Monad in
Control.Monad.Cont - Icon, Unicon :
create, suspend, @operator: coexpressions - Parrot:
ContinuationPMC; uses continuation-passing style for all control flow - Perl: Coro and Continuity
- Pico:
call(exp())andcontinue(aContinuation, anyValue) - JavaScript Rhino :
Continuation - Ruby:
callcc - Scala:
Responder - Scheme:
call-with-current-continuation(commonly shortened tocall/cc) - Smalltalk:
Continuation currentDo:, in most modern Smalltalk environments continuations can be implemented without additional VM support. - Standard ML of New Jersey:
SMLofNJ.Cont.callcc - Unlambda:
c, the flow control operation for call with current continuation - C#:
asyncandawait: “sign up the rest of method as the continuation, and then return to your caller immediately; the task will invoke the continuation when it completes.” Asynchronous Programming for C#
In any language which supports closures and proper tail calls, it is possible to write programs in continuation-passing style and manually implement call/cc. (In continuation-passing style, call/cc becomes a simple function that can be written with lambda.) This is a particularly common strategy in Haskell, where it is easy to construct a "continuation-passing monad" (for example, the Cont monad and ContT monad transformer in the mtl library). The support for proper tail calls is needed because in continuation-passing style no function ever returns; all calls are tail calls.
Continuations in Web development
One area that has seen practical use of continuations is in Web programming.[6][7] The use of continuations shields the programmer from the stateless nature of the HTTP protocol. In the traditional model of web programming, the lack of state is reflected in the program's structure, leading to code constructed around a model that lends itself very poorly to expressing computational problems. Thus continuations enable code that has the useful properties associated with inversion of control, while avoiding its problems. Inverting back the inversion is a paper that provides a good introduction to continuations applied to web programming.
Some of the more popular continuation-aware Web servers are the Racket Web Server, the UnCommon Web Framework and Weblocks Web framework for Common Lisp, the Seaside framework for Smalltalk, Ocsigen/Eliom for OCaml, Continuity for Perl, Wee for Ruby, and the Nagare framework for Python. The Apache Cocoon Web application framework also provides continuations (see the Cocoon manual).
Kinds of continuations
Support for continuations varies widely. A programming language supports re-invocable continuations if a continuation may be invoked repeatedly (even after it has already returned). Re-invocable continuations were introduced by Peter J. Landin using his J (for Jump) operator that could transfer the flow of control back into the middle of a procedure invocation. Re-invocable continuations have also been called "re-entrant" in the Racket language. However this use of the term "re-entrant" can be easily confused with its use in discussions of multithreading.
A more limited kind is the escape continuation that may be used to escape the current context to a surrounding one. Many languages which do not explicitly support continuations support exception handling, which is equivalent to escape continuations and can be used for the same purposes. C's setjmp/longjmp are also equivalent: they can only be used to unwind the stack. Escape continuations can also be used to implement tail-call optimization.
Disadvantages
Continuations are the functional expression of the GOTO statement, and the same caveats apply.[8] While they are a sensible option in some special cases such as web programming, use of continuations can result in code that is difficult to follow. In fact, the esoteric programming language Unlambda includes call-with-current-continuation as one of its features solely because of its resistance to understanding. The external links below illustrate the concept in more detail.
Linguistics
Some phenomena in natural languages have been described using the notion of delimited continuation.
Informally speaking, continuations can account for the similarity between such sentences as "Alice sees Bob"—formally, 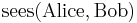 —and "Alice sees everyone", i.e.
—and "Alice sees everyone", i.e. 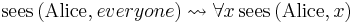 .
.
See Chris Barker's paper Continuations in Natural Language for details. See also Montague grammar.
See also
- Call-with-current-continuation
- Closure
- COMEFROM
- Continuation-passing style
- Control flow
- Coroutine
- Delimited continuation
- Denotational semantics
- GOTO
- Spaghetti stack
References
- ^ "Call with current continuation for C programmers". Community-Scheme-Wiki. 12 October 2008. http://community.schemewiki.org/?call-with-current-continuation-for-C-programmers.
- ^ a b c d Reynolds 1993
- ^ "Steve "Slug" Russell". Computer History. http://www.computernostalgia.net/articles/steveRussell.htm.
- ^ Palmer, Luke (June 29, 2004). "undo()? ("continuation sandwich" example)". perl.perl6.language (newsgroup). http://groups.google.com/group/perl.perl6.language/msg/b0cfa757f0ce1cfd. Retrieved 2009-10-04.
- ^ Haynes, C. T., Friedman, D. P., and Wand, M. 1984. Continuations and coroutines. In Proceedings of the 1984 ACM Symposium on LISP and Functional Programming (Austin, Texas, United States, August 06–08, 1984). LFP '84. ACM, New York, NY, 293-298.
- ^ [1]
- ^ [2]
- ^ Quigley, John (September 2007). "Computational Continuations" (PDF). p. 38. http://www.jquigley.com/files/talks/continuations.pdf.
Further reading
- Peter Landin. A Generalization of Jumps and Labels Report. UNIVAC Systems Programming Research. August 1965. Reprinted in Higher Order and Symbolic Computation, 11(2):125-143, 1998, with a foreword by Hayo Thielecke.
- Drew McDermott and Gerry Sussman. The Conniver Reference Manual MIT AI Memo 259. May 1972.
- Daniel Bobrow: A Model for Control Structures for Artificial Intelligence Programming Languages IJCAI 1973.
- Carl Hewitt, Peter Bishop and Richard Steiger. A Universal Modular Actor Formalism for Artificial Intelligence IJCAI 1973.
- Christopher Strachey and Christopher P. Wadsworth. Continuations: a Mathematical semantics for handling full jumps Technical Monograph PRG-11. Oxford University Computing Laboratory. January 1974. Reprinted in Higher Order and Symbolic Computation, 13(1/2):135—152, 2000, with a foreword by Christopher P. Wadsworth.
- John C. Reynolds. Definitional Interpreters for Higher-Order Programming Languages Proceedings of 25th ACM National Conference, pp. 717–740, 1972. Reprinted in Higher-Order and Symbolic Computation 11(4):363-397, 1998, with a foreword.
- John C. Reynolds. On the Relation between Direct and Continuation Semantics Proceedings of Second Colloquium on Automata, Languages, and Programming. LNCS Vol. 14, pp. 141–156, 1974.
- Reynolds, John C. (1993). "The discoveries of continuations". Lisp and Symbolic Computation 6 (3/4): 233–248. ftp://ftp.cs.cmu.edu/user/jcr/histcont.pdf.
- Gerald Sussman and Guy Steele. SCHEME: An Interpreter for Extended Lambda Calculus AI Memo 349, MIT Artificial Intelligence Laboratory, Cambridge, Massachusetts, December 1975. Reprinted in Higher-Order and Symbolic Computation 11(4):405-439, 1998, with a foreword.
- Robert Hieb, R. Kent Dybvig, Carl Bruggeman. Representing Control in the Presence of First-Class Continuations Proceedings of the ACM SIGPLAN '90 Conference on Programming Language Design and Implementation, pp. 66–77.
- Will Clinger, Anne Hartheimer, Eric Ost. Implementation Strategies for Continuations Proceedings of the 1988 ACM conference on LISP and Functional Programming, pp. 124–131, 1988. Journal version: Higher-Order and Symbolic Computation, 12(1):7-45, 1999.
External links
- ACM SIGPLAN Workshop on Continuations 2011 at the ICFP.
- Continuations for Curmudgeons by Sam Ruby
- Teach Yourself Scheme in Fixnum Days by Dorai Sitaram features a nice chapter on continuations.
- Continuations and Stackless Python by Christian Tismer
- On-line proceedings of the Fourth ACM SIGPLAN Workshop on Continuations
- On-line proceedings of the Second ACM SIGPLAN Workshop on Continuations
- Continuation, functions and jumps
- http://okmij.org/ftp/continuations/ by Oleg Kiselyov
- Rhino With Continuations
- Continuations in pure Java from the RIFE web application framework
- Debugging continuations in pure Java from the RIFE web application framework
- Comparison of generators, coroutines, and continuations, source of the above example